Alexander Reelsen
Distributed search under the hood
#1about 3 minutes
Understanding the benefits of distributed systems
Distributed systems offer advantages like load sharing, increased reliability through redundancy, and faster processing via parallelization.
#2about 5 minutes
Navigating the complexities of distributed computing
Moving from a single machine to a distributed environment introduces significant complexity in communication, coordination, and error handling, as highlighted by the fallacies of distributed computing.
#3about 3 minutes
How distributed systems achieve consensus
Consensus algorithms are crucial for maintaining a consistent state across all nodes, enabling tasks like cluster membership management, data writes, and leader election.
#4about 4 minutes
Introducing the core principles of Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a distributed search engine built for speed, scale, and relevance, offering resiliency and flexibility for use cases from e-commerce to observability.
#5about 5 minutes
Managing the cluster with a master node
Elasticsearch uses a master node to manage the cluster state, which includes node membership and data placement, and distributes this state to all nodes to ensure a consistent view.
#6about 3 minutes
Distributing data using shards and replicas
Data in Elasticsearch is partitioned into shards, with replica shards providing redundancy and read scalability, allowing the system to scale horizontally.
#7about 2 minutes
Understanding the two-phase distributed search process
A search request is handled in two phases, first querying all relevant shards for top results and then fetching the full documents from only the necessary shards.
#8about 1 minute
Optimizing query routing with adaptive replica selection
Instead of random routing, adaptive replica selection improves query performance by sending requests to shards on less busy nodes based on their recent response times.
#9about 3 minutes
Accelerating top-k queries with result skipping
Search performance can be dramatically improved by dynamically optimizing queries to skip documents that cannot possibly make it into the top results, at the cost of an exact total hit count.
#10about 3 minutes
Navigating the challenges of distributed aggregations
Calculating aggregations like term counts across distributed shards is complex and can lead to inaccuracies if not all data is considered, requiring careful handling of partial results.
#11about 3 minutes
Efficient aggregations with probabilistic data structures
Probabilistic data structures like HyperLogLog++ and T-Digest enable memory-efficient cardinality and percentile aggregations by trading perfect accuracy for significantly reduced resource usage.
#12about 5 minutes
Embracing trade-offs in distributed system design
Building and operating distributed systems involves accepting trade-offs between consistency, availability, and performance, making it crucial to understand the specific behaviors of your chosen system.
#13about 6 minutes
Answering questions on Elasticsearch internals
The Q&A session covers Elasticsearch's custom consensus algorithm, data placement using MurmurHash, and the role of tokenizers in text analysis.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
Wilken GmbH
Ulm, Germany
Senior
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Kubernetes
+1
Matching moments
03:31 MIN
Q&A on indexing, aggregations, and OpenSearch vs Elasticsearch
Search and aggregations made easy with OpenSearch and NodeJS

03:30 MIN
Understanding OpenSearch core concepts and architecture
Search and aggregations made easy with OpenSearch and NodeJS
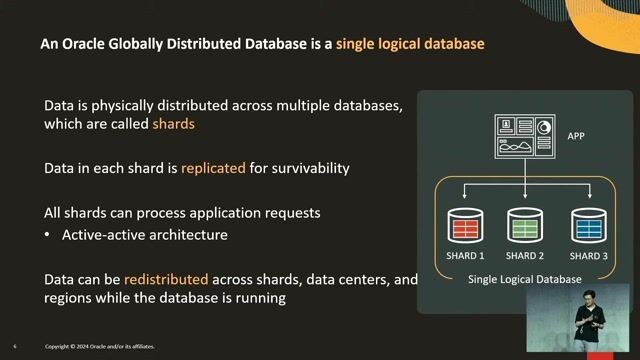
03:09 MIN
How a distributed database works under the hood
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

03:35 MIN
How distributed systems increase infrastructure complexity
Databaseless Data Processing - High-Performance for Cloud-Native Apps and AI

03:03 MIN
Understanding the fundamentals of distributed SQL databases
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
05:26 MIN
Understanding the fundamentals of the Elasticsearch search engine
Add Location-based Searching to Site with ElasticSearch
01:24 MIN
Understanding the primary use cases for distributed databases
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

26:30 MIN
Q&A: Key skills, complex projects, and the future of tech
Retooling and refactoring - an investment in people.
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 45:13
45:13Add Location-based Searching to Site with ElasticSearch
Derek Binkley
 28:39
28:39Make Your Data FABulous
Philipp Krenn
 50:06
50:06Single Server, Global Reach: Running a Worldwide Marketplace on Bare Metal in a Cloud-Dominated World
Jens Happe
 1:05:44
1:05:44WeAreDevelopers LIVE - Vector Similarity Search Patterns for Efficiency and more
Chris Heilmann, Daniel Cranney, Raphael De Lio & Developer Advocate at Redis
 28:41
28:41Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
Wei Hu
 24:53
24:53Don't Change the Partition Count for Kafka Topics!
Dainius Jocas
 41:56
41:56What the Heck is Edge Computing Anyway?
Austin Gil
 32:46
32:46Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
Wei Hu
Related Articles
View all articles



From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.

Referral Board
Charing Cross, United Kingdom
Java
Solr
Elasticsearch
Continuous Integration

E. Breuninger GmbH & Co.
Berlin, Germany
Remote
Senior
Java
Solr
Kotlin
Laravel
+1

E. Breuninger GmbH & Co.
Düsseldorf, Germany
Remote
Senior
Java
Solr
Kotlin
Laravel
+1

E. Breuninger GmbH & Co.
Hamburg, Germany
Remote
Senior
Java
Solr
Kotlin
Laravel
+1

E. Breuninger GmbH & Co.
München, Germany
Remote
Senior
Java
Solr
Kotlin
Laravel
+1

SECUSTAFF GmbH
Osnabrück, Germany
Linux
Docker
Kubernetes
Elasticsearch

About You
Berlin, Germany
€60-70K
Intermediate
API
MySQL
NoSQL
React
+8

Adecco
Quinton, United Kingdom
Remote
Intermediate
GIT
DevOps
Ansible
Terraform
+2

Adecco
Quinton, United Kingdom
Remote
Intermediate
GIT
DevOps
Ansible
Terraform
+2